Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism
Drawing alkyne formulas from names. Drawing alkene formulas from names.
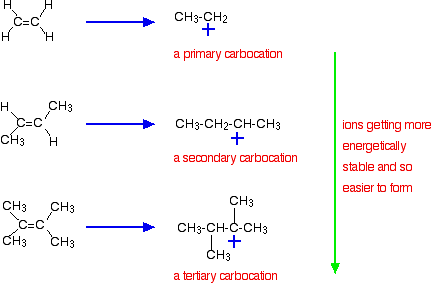
9 2 Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Symmetrical Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts
The Role of the Solvent in S N 1 S N 2 E1 and E2 Reactions.

. Hydrohalogenation is the addition of hydrogen halides such as HCl or HI to alkenes to yield the corresponding haloalkanes. Mechanism The mechanism of the reaction involves the following three steps. Hindered halides is a challenge in organic synthesis.
Drawing formulas from names. A stereochemical study revesled. Delydrobalogenation of vinyi halides is essentially an E2 process.
Mechanism of Dehydration of Alcohols. Matching alcohols to their names I. Hydrogen halides react with alkynes in the same manner as they do with alkenes.
Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols. Nitrogen and sulfur nucleophiles will give S N 2 substitution in the case of 1º and 2º-halides. Drawing formulas from names.
There are 3 mechanisms suggested for the elimination reactions. Given that i Ni0 complexes undergo oxidative addition more readily than NiI complexes with aryl halides and ii NiII complexes are believed to rapidly engage with sp 3 carbon-centered radicals to form NiIII species enabling sp 3 sp 2 and sp 3 sp 3 CC bond formations 15 16 we favor the dual-catalysis mechanism outlined. All these eliminations are β- eliminations.
Markovnikovs Rule with Practice Problems. Inversion results because the pyridine reacts with ROSOCl to give ROSONC 5 H 5 before anything further can take place. 1212 Structure of the Carbonyl.
C n H 2n. Thus the carbonyl carbon and the three atoms attached to it lie in the same plane and the π-electron cloud is above and below this plane. A recent application is the generation of highly reactive aryl radicals which are useful arylating reagents in synthesis by photoinduced electron transfer PET from photoredox catalysts to suitable precursors followed by bond scission 8 9However the choice of aryl radical precursors is currently limited to electron-poor arenes such as diazonium 6 10 or.
In addition the oxygen atom also has two non bonding electron pairs. Oxidative addition of aryl and alkyl halides to a reduced iron pincer complex. Secondary alcohols get oxidized to ketones and primary are oxidized to carboxylic acids by chromic acid.
If the two carbon atoms at the double bond are linked to a different number of hydrogen atoms the halogen is found preferentially at the carbon with fewer hydrogen. It is a subset of reactions that very closely resembles the insertion reactions and both are differentiated by the mechanism that leads to the resulting stereochemistry of the products. Because the hydrogen is absorbed on the catalyst surface.
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes with Practice Problems. From alkenes i By acid catalysed hydration. A migratory insertion is a type of reaction in organometallic chemistry wherein two ligands on a metal complex combine.
In case of unsymmetrical alkenes the addition reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikovs rule Unit 13 Class XI. Drawing formulas from names. Benzyl C 6 H 5 CH 2.
CH 3 CHCH 2 HI CH 3 CHICH 2 H. However often the two are used interchangeably because the. Formation of alkenes.
3º-halides will probably give E2 elimination with nitrogen nucleophiles they are bases. As shown in the following figure a hydrogen ion catalyzes the Markovnikovs addition. The mechanism of alkyne hydrogenation is identical to that of the alkenes.
Preparation of Hydrocarbons Alkenes. Water hydrolysis will be favorable for 2º 3º-halides. S N 1 S N 2 E1 or E2 the Largest Collection of Practice Problems.
Evidence for this mechanism is as follows. The addition of hydrogen bromide to 1butyne gives 2bromo1butene as the major product of the first step. The elements of water can be added to the doublebonded carbons of an alkene in either a Markovnikovs or an antiMarkovnikovs manner.
Electrophilic addition to conjugated dienes occurs through 12 and 14-addition mechanism out of Q. The bond angles are approximately 120 as expected of a trigonal coplanar structure Figure 121. HBr and HCl to form alkyl halides.
Alcohol dehydration is an example of an elimination reaction which is quite the opposite of substitution reaction and addition reaction. Primary aliphatic amines can be cleanly mono-alkylated by. The antiMarkovnikovs addition results from a hydroborationoxidation reaction.
S N 1 S N 2 E1 E2 How to Choose the Mechanism. Drawing alcohol formulas. In high dielectric ionizing solvents S N 1 and E1 products may be formed.
Addition Reactions of Alkenes. Microwave heating enables a Borrowing Hydrogen strategy to form C-N bonds from alcohols and amines removes the need for solvent and reduces the reaction times while the results are comparable with those using thermal heating. The addition of pyridine to the mixture of alcohol and thionyl chloride results in the formation of alkyl halide with inverted configuration.
Most of the reactions involving the preparation of alkenes involve elimination process. This concept of redox active ligands has resulted in new base metal catalysts for the asymmetric hydrogenation of alkenes as well as the hydrosilylation and hydroboration of olefins.
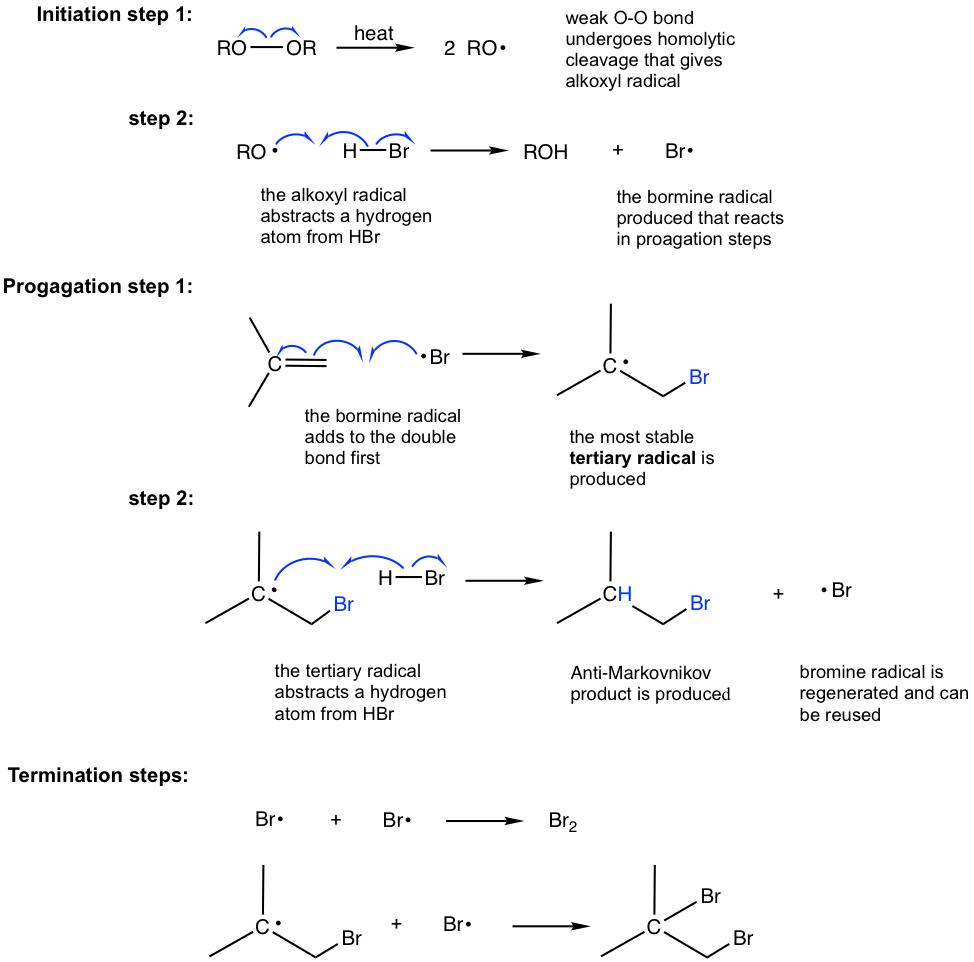
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
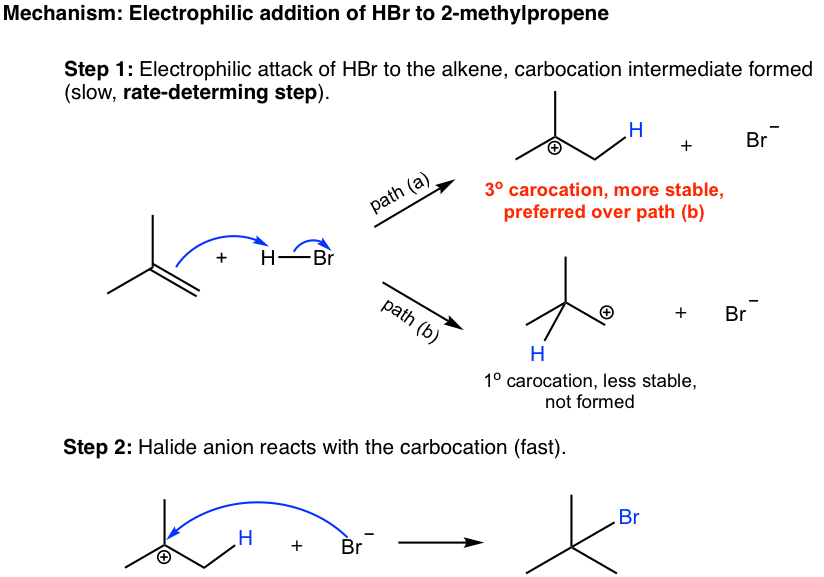
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I

Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Youtube

Electrophilic Addition Reactions Of Alkenes Mcc Organic Chemistry
No comments for "Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism"
Post a Comment